Luis Alvarez
The 1970’s brought many wonders to the world in the science field; Luis Alvarez is one of those wonders. He invented the synchrotron, made the three radar systems, and discovered the “resonance states” of particles. Although most people remember him for these things, he’s most famous for his theory on the K/T extinction with his son, Walter, who is a geologist. These contributions shaped the minds of many other scientists and, even society.
Luis Alvarez was born in San Francisco, California on June 13, 1911. He went to the University of Chicago and graduated with a B. Sc in 1932. Later on he joined the Radiation Laboratory of the University of California. He co-discovered the “East-West Effect”, which was detected in charged cosmic rays and was used to infer the charge. But his very first invention was the synchrotron, which was the first particle accelerator. Although he was considered an “amateur” for his impact on paleontology and being an accomplished physicist, he gave hope and reason to many when he came up with K/T theory. His theory was that the reason the dinosaurs became extinct was because there was a huge explosion of a large comet or meteor that threw up tons of dust, blotted out the sun, and caused earth’s vegetation to wither. Without the vegetation, animals had nothing to eat and started dying off. This left the dinosaurs with nothing to survive off of, which caused them to become extinct. When this theory was introduced to the society, many people were baffled that they never though about something like that. The entire puzzle piece fit in the puzzle. Now the theory is widely accepted among scientists and others. He continued his life trying to find more significant evidence for his theory with his son. Alvarez’s life came to an end when he was overly exposed to radiation. We do know that he had cancer, but it is uncertain for how long or what type of cancer he had. He left behind his family and a theory we will all remember, the K/T theory.
Bibliography
“Luis Alvarez” The Nobel Prize in Physics 1968.
http://nobelprize.org/nobel prizes/physics/laureates/1968/alvarez-bio.html 15 May 2009
“Luis Walter Alvarez.” The Free Encyclopedia.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Luis Walter Alvarez 17 May 2009
“Impact Theory.” The Alvarez Hypothesis
http://hoopermuseum.earthsci.carleton.ca/saleem/meteor.htm 17 May 2009
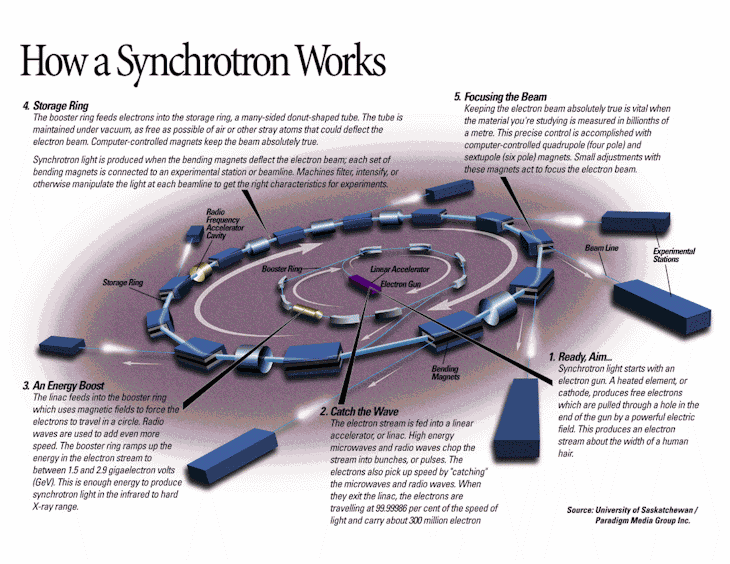
Synchroton Alvarez invented
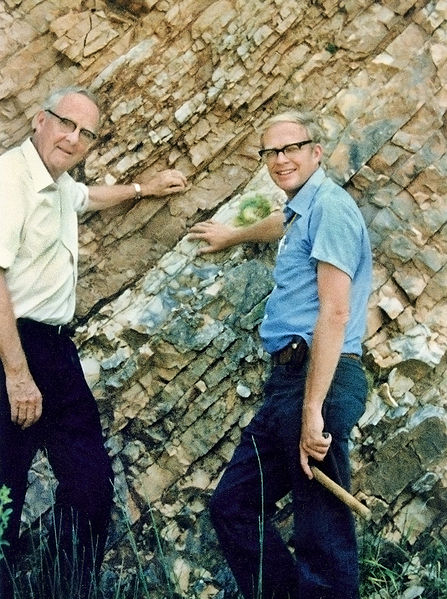

Luis Alvarez with his son, Walter

K/T Theory